Technology is constantly evolving, and, if you run a tech company, you will know that your company has to evolve on a near constant level...
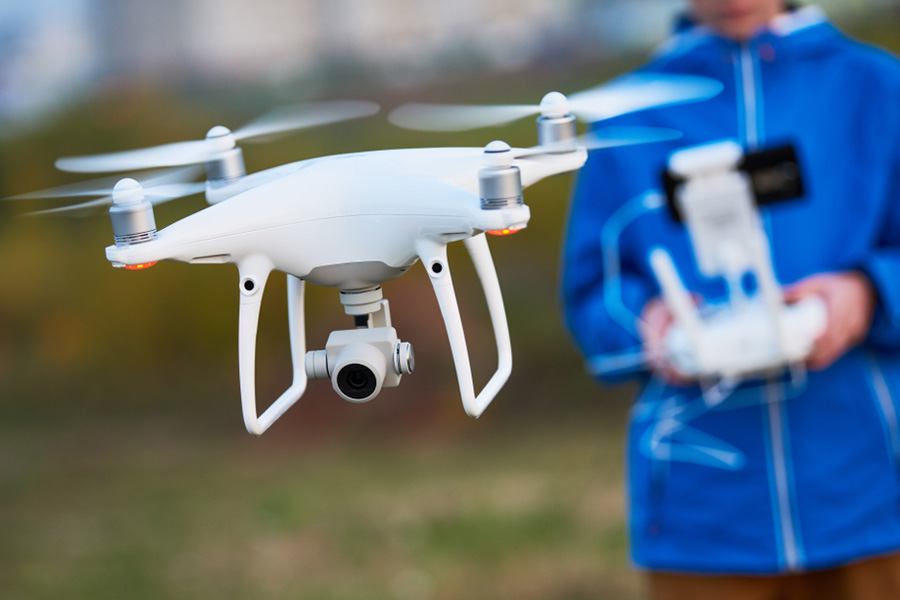
How you can improve your drone speed easily
Today the drone has transformed the youth into a fun way. They are not interested in car or bike. For They want high – tech...
How to Create your own Hashtag on Facebook
From the billboard signs on the roads to the eating menus in the restaurants, hashtags have struck all the things by storm. A decade ago,...
Six Problems Modern Medicine Can’t Solve (that your Faith can!)
Today, in the 21st century, many downplay the health benefits of religious commitment, faith, and any sort of spirituality. In this article, I’m going to...
The era of the bitcoin revolution
According to the authentic reports as well as authentic sources, it is been said that no one knows who invented bitcoin, or at least the...
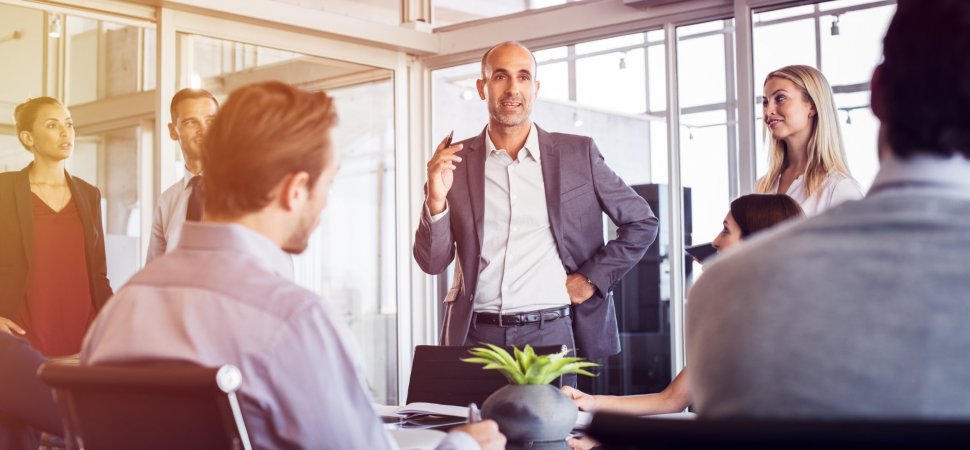
Six Tips For Being A Better Business Leader
Being a good business leader can be difficult, and not everyone is up to the task. Although it can be challenging and a lot of...
5 Tips on how to Save Gel Blaster Batteries
Gel blasting is a sport similar to paintball that is often played in local clubs by people who enjoy the thrill of this game. It...
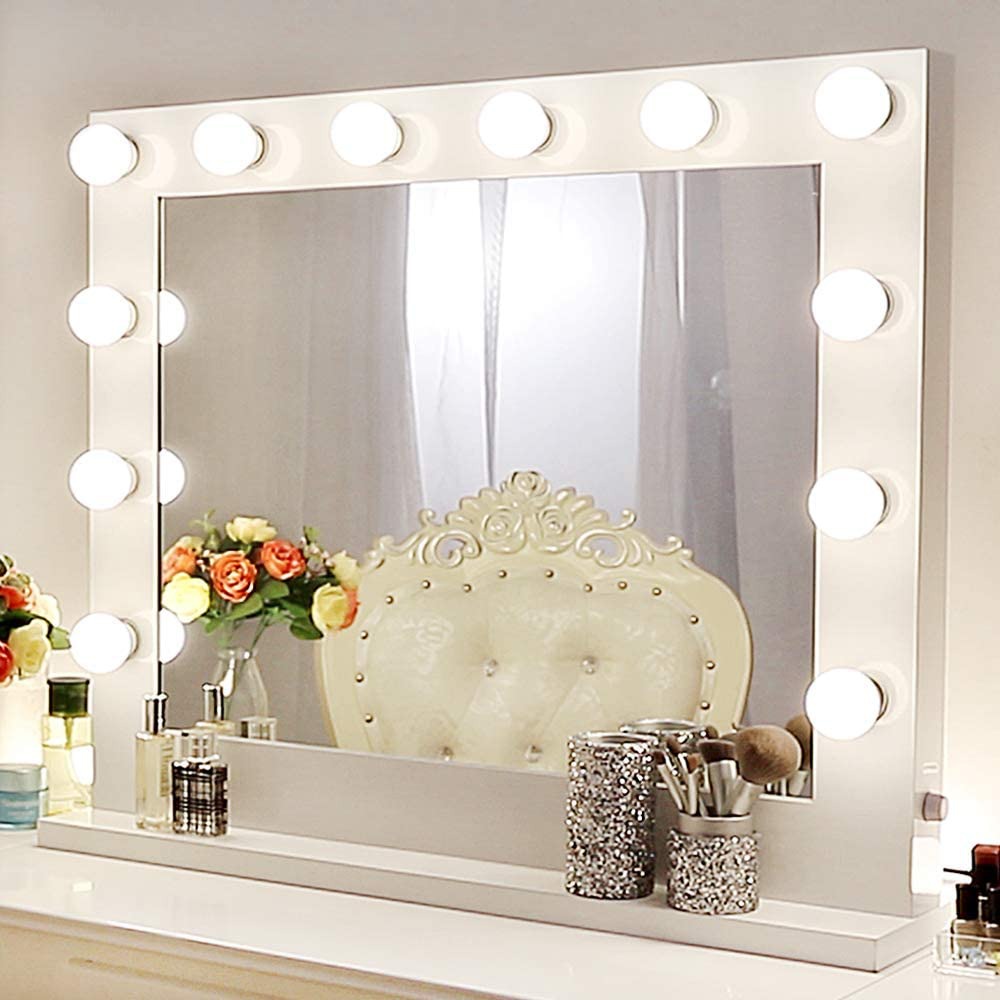
Various types of mirrors for your bathroom
A mirror is one of the most essential elements for a bathroom and it is not only required for reflective functionality but it can also...
All you need to know about bitcoin
The following are some of the most important as well as top features as well as characteristics of the bitcoin, which is a digital currency:...
Tips to avoid the fake and spam followers
In the period of cover-19 restriction, the number of the population become jobless and hopeless. In this painful time, the only hope of dawn is...